IoT or the Internet of Things refers to all physical devices around the world that are connected to the internet and can share and collect data. Whether it’s an air conditioning unit that you operate with your smartphone, a driverless train that ferries hundreds of people, or even remote patient monitoring by doctors, the IoT includes all of these capabilities that link hardware to wireless networks.
Interestingly, you’ll note that the IoT includes devices that wouldn’t conventionally be attached to internet phone systems or have the capability of functioning without human involvement. For example, the air conditioner and the train. Over time, these devices were fitted with sensors to capture data and operate via wireless networks.
It’s almost impossible to separate Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology from the IoT as it powers most automated functions and revolutionizes information sharing and business processes. AI can also convey real-time data and facilitate most processes of data analytics technology.
In a startling statistic, Cybersecurity Ventures has predicted the global cost of cybercrime to grow to $10.3 trillion by 2025. Technology is a double-edged sword. While, on the one hand, it has unlocked immense potential for automating and scaling up business and, by that extension, productivity, it has also exposed our systems to an unparalleled threat from cyber crimes.
AI technology is multi-faceted and, when related to the IoT, is used for automation testing and solutions like sap cloud platform integration, as well as providing security to the IoT framework. The catch here is that the defenses in terms of tech solutions available to us are also available to hackers.
This is why weighing the benefits and drawbacks of AI in IoT cybersecurity is pertinent.
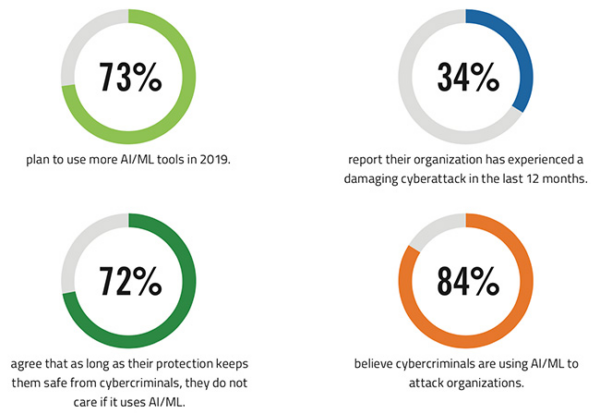
Image Sourced from helpnetsecurity.com
Benefits of AI in IoT Cybersecurity
By and large, AI and machine learning technology can use automated software testing for threat detection that is more effective than traditional software solutions. Here are some of the main benefits of AI:
Detection of New Threats
AI systems are now being fitted with advanced algorithms that can detect malware, run pattern recognition, and spot ransomware threats long before they enter a system. AI uses natural language processing (NLP) to provide a high level of predictive intelligence. It uses RPA tech to independently scan through large volumes of articles, studies, and news on cyber threats to collate data.
This provides information on any new glitches, as well as prevention strategies. AI technology, in fact, is so advanced that it has intelligence on global as well as domain-specific security threats. With this information, AI-powered security systems can predict the most likely threat to your system.
Large Volume Data Handling
AI technology enables handling a large volume of data, which is simply impossible for human resources to match. According to a recent report, 230,000 new malware samples are generated daily, which is expected to keep rising in the coming years. This necessitates a robust cyber security system to preempt and protect against large-scale attacks.
AI and machine learning technology are equipped with sophisticated algorithms that can scour large volumes of data to detect malware threats in a fraction of the time it would take manually.
AI Provides Better Endpoint Protection
With more and more companies adopting remote working, AI is needed to secure the endpoints of all these machines connecting to the IoT. While VPNs and other antivirus software can protect against malware attacks, they work on signatures. So, it’s essential to stay on top of signature definitions to stay protected against the latest threats.
This can potentially be a problem if there’s a lag in virus definitions due to either a failure to update the antivirus solution or a lack of awareness from the software vendor. In this case, signature protection may not be able to protect against a new type of malware attack.

Image Sourced from financesonline.com
Manage Bots
Bots are one of the most popular features of AI and are used across various business processes, including sales and marketing and calculating CSAT. However, malicious bots can also be potential security hazards leading to data fraud and information theft due to stolen credentials and fake accounts.
It’s not possible to counter automated threats with manual responses alone. AI and machine learning can distinguish between reliable bots like search engine crawlers and malicious bots. With AI, it’s possible to analyse large volumes of data, enabling cybersecurity teams to adapt their strategy according to the need of the hour.
IoT vulnerabilities from automated threats like bots can indeed be countered with AI technology.
Now that we’ve looked at AI’s benefits in IoT cybersecurity let’s consider some of the drawbacks.
Drawbacks of AI in IoT Cybersecurity
AI, by nature, is a constantly evolving technology. This makes it hard to gauge its exact potential and also throws up questions about its role in cybersecurity. This is because:
It’s AI Vs. Hackers
While we can benefit from harnessing the evolving possibilities of AI tech, the same opportunities are also available to cyber criminals.
Unsurprisingly, the same tech that can be used to safeguard businesses against security threats can wreak havoc in the wrong hands. Unfortunately, this is something that is beyond our control. AI that accelerates digital transformation is just as likely to infiltrate security systems and cause irrevocable damage.
Cybercriminals can use machine learning to determine how AI solutions are designed to guard against infringement. Fuzzing is a popular program analysis technique that hackers use to find weak spots in software. With fuzzing, they can infiltrate a target program with malicious input designed to cause system crashes, memory errors, and buffer overflows.
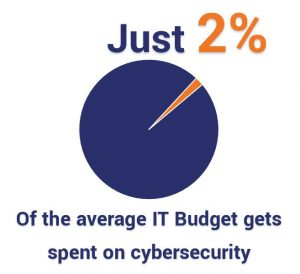
Image Sourced from thesslstore.com
They then use the same tech to adapt malware to make it look harmless. This way, when IT teams scan for system threats, they overlook the “harmless” malware and instead focus on what they perceive as more serious threats.
High Adoption Costs
Although AI is being adopted into many business processes, its adoption in IoT cybersecurity is not that commonplace. This is because AI adoption is expensive.
Building and maintaining an AI-backed tech framework for IoT cybersecurity requires large investments in infrastructure— for building data centres, computer memory, and cloud-based contact centre solutions, among other things. Such financial resources are not available to all small and medium-sized businesses.
Also, AI development is a direct result of big data and data science, and the IT experts working in these super-specialized fields are not accessible to many businesses.
Another challenge in adopting AI for IoT security is that businesses using this tech have certain compliance regulations. Hackers, however, are not bound by any such regulations and can use and abuse AI technology at will.
Cyber Threats Get More Complex
Every day, hackers and their techniques get more sophisticated. According to a recent report, an estimated 65,000 hacking attempts are made on small and medium businesses (SMBs) in the UK, of which roughly 4500 are believed to be successful. This involves 1.6 million of the existing 5.7 million SMBs in the UK.
AI solutions are generally put through intensive research before they can go to market. Researchers open-source their projects and publish them in open journals so that everyone can access them. Unfortunately, this includes hackers, who can use this information to plan more sophisticated attacks.
While it is impossible to prevent every attack, AI solutions for IoT security regulation need to be regularly updated to keep up with the growing complexity of risks.
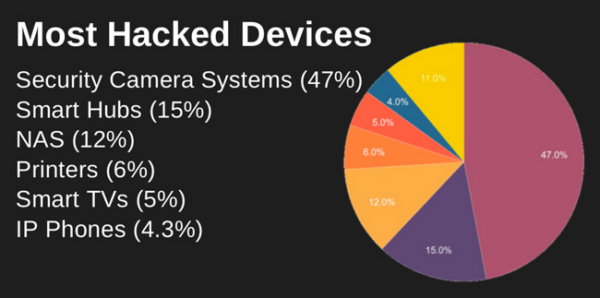
Image Sourced from devopedia.org
Unemployment
This is a controversial issue regarding any type of automation. Tools like IBM automation can help companies scale up without reducing effectiveness or efficacy. The likelihood of companies replacing human labour entirely may still be a stretch. However, there’s no denying that AI is creeping into most workflows because of how it eliminates the risk of human error and by virtue of its scalability.
For IoT cybersecurity, companies (those who can afford it) are starting to prefer AI solutions instead of hiring IT professionals to test and troubleshoot their networks.
Balancing The Risks & Rewards of AI in IoT Cybersecurity
Having looked at the different benefits and drawbacks of AI in IoT cybersecurity, it’s safe to say that despite its challenges, AI adoption is still a viable option for safeguarding the network and data security. With more and more companies taking their workflows online, the threat of cyber crimes is higher than ever before.
From very simple online functions like how to make an electronic signature to highly classified cloud computing cases, almost everything is open to some form of cyber threat.
The only way to stay ahead in the race versus criminals is to keep up with the latest tech innovations. Granted, they might have the same access and could potentially beat you at our own game, but those are still better odds than not being equipped with the best defence in the first place.
Check out all the software testing webinars and eBooks here on EuroSTARHuddle.com
About the Author:
 Becca Uptmor is the Senior Director of Web Marketing at Databricks, specializing in everything from website redesigns and azure data lake storage to international SEO and global content marketing campaigns. With decades of experience within the marketing industry, Becca is known for successfully facilitating the growth of a company on a global scale.
Becca Uptmor is the Senior Director of Web Marketing at Databricks, specializing in everything from website redesigns and azure data lake storage to international SEO and global content marketing campaigns. With decades of experience within the marketing industry, Becca is known for successfully facilitating the growth of a company on a global scale.
